What is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B (HBV) is a chronic condition that has become a worldwide problem. The disease can cause severe damage to the liver and other serious conditions like HCC (hepatocellular cellular carcinoma). About 50% of people infected with Hepatitis B do not know they are infected. This causes the disease to spread to others who are not infected as it is spread through body fluids and blood.
Acute Hepatitis B lasts for less than six months, and chronic Hepatitis B lasts longer than six months. The chronic condition increases the risk of liver failure, liver cancer and cirrhosis.
If the condition is treated quickly the recovery is good. If left untreated, it can cause eventual health complication and death.
Advances in vaccination has helped in developing vaccines to manage Hepatitis B. It is important to get treatment so individuals who are infected do not spread the disease to others.
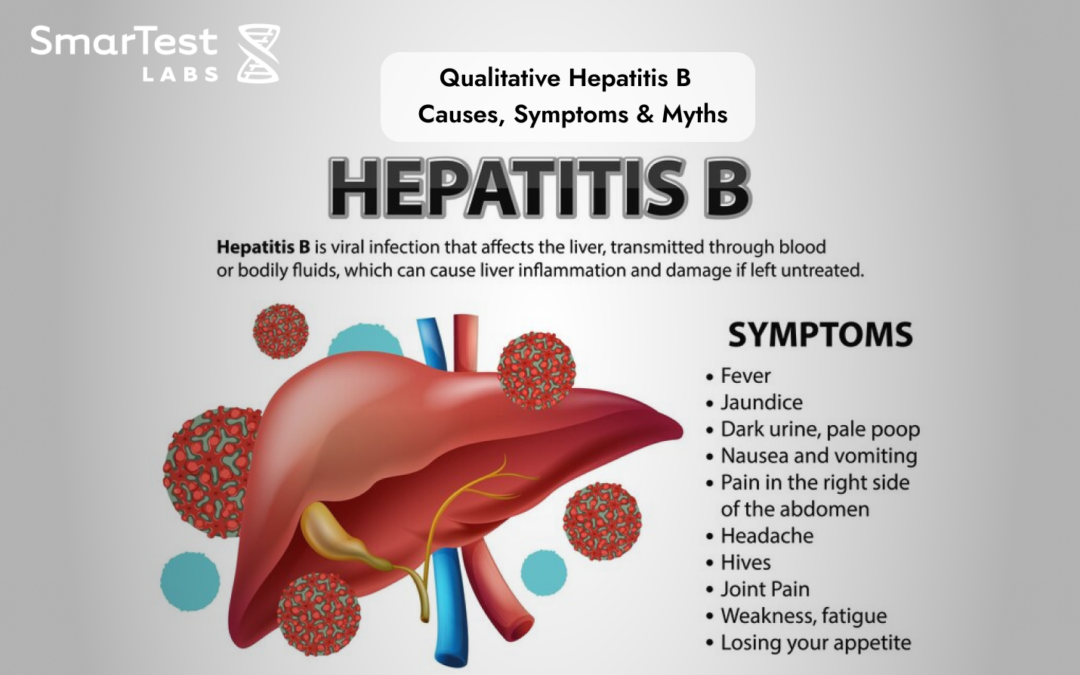
What are some of the Signs and symptoms
Symptoms of Hepatitis B often do not show quickly. The symptoms could take up to 90 days to years to manifest symptoms.
Some of the symptoms that need to be tested are as follows:
- Exhaustion
- Discolored urine (dark color)
- Fever
- Lack of appetite
- Stomach pain and nausea
- Yellow and jaundiced eyes.
How is Hepatitis B spread?
The Hepatitis B virus is spread through body fluids from an infected person. This includes contact with blood from an infected person.
Other ways that the virus spreads are through drug use via injections from infected needles. Mothers who are infected with Hepatitis B can also pass the virus to their unborn child infecting the child from birth.
Who are at Risk of Contracting Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B can infect anyone who is not careful However, there is science that shows that Hepatitis B is more pronounced inn certain groups of people.
Per the Centers of Disease Control (CDC) these categories could include the following:
- New born Infants whose parents had Hepatitis B
- People in certain countries with High cases of Hepatitis B.
- People with HIV
- People on Dialysis
- People with liver damage
- People in the prison system
- People who are sharing needles with others
- Health Care workers who are exposed to blood.
How can Hepatitis B be prevented?
It is proven that vaccination is the most effective way to avoid the disease. The vaccination is administered in three doses and a person must take all 3 doses (this can vary with the brand of vaccine).
CDC recommends the following groups get vaccinated against hepatitis B:
- All infants.
- All individuals younger than 19 who have not been vaccinated.
- Adults ages 19–59.
- Adults ages 60 and older at higher risk for hepatitis B
Screening and testing should be done through a blood test. If the test determines that a person is not immune the recommendation is to get the Hepatitis B vaccination.
What are some of the myths of Hepatitis B
If a person does not have symptoms, it does not mean they are not infected.
If a person is a carrier of the virus, they can still infect others although they may not show symptoms.
Chronic Hepatitis B people who have the virus for 6 months cannot get re-infected.
Although HBV virus resides in the salvia of a person, it cannot be spread through sneezing, kissing, coughing, food or water.
How can SmarTest Labs Help?
At our laboratory we have qualified testers who can gather a sample of your blood called titers. This then will be tested to determine if a person is infected, has immunity or not infected and requires vaccination.
We can guide you through the process as the vaccine requires numerous doses and must be spread at pre-determined intervals.
Please call us for guidance at 301-686-8566 or send us an email at contact@smartestlabs.com
Recent Comments